Differences in Image Quality between 4:2:2 and 4:2:0 Chroma Formats in Cascaded Codec Connections
For the live broadcasting of sports or other events from the venue itself, video codec systems are generally connected in cascade (for multiple encoding and decoding), as shown in Figure 1 below, to deliver images recorded by the cameras to TV viewers.
To limit degradation in the quality of the video images delivered to viewers, it is essential that any image quality degradation that may be caused by the use of cascaded codec systems be minimized.
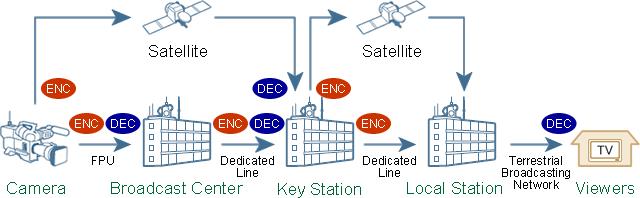
Figure 1: Example process for the delivery of live images to viewers
Comparison of image quality of AVC/H.264 High Profile and High 4:2:2 Profile in cascaded codec connection
The following section compares the image quality of AVC/H.264 High Profile, which is incompatible with the 4:2:2 chroma format, and that of High 4:2:2 Profile, which is compatible with this format.
The three parts (Ⓐ, Ⓑ, and Ⓒ) of Image 1 on the under were compared to assess the image quality obtained with 4:2:2 chroma format and that obtained with 4:2:0 chroma format for three successive encoding/decoding operations.
Image 1: Three parts of the image that were compared
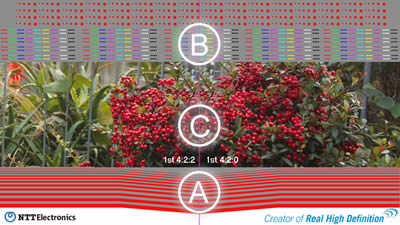
A comparison was made of the image quality for parts A, B, and C. The resolution of the whole image was 1920 x 1080.
Compatible with AVC/H.264 High 4:2:2 Profile
HV9100 Series: Minimizes Image Quality Degradation in Cascaded Codec Connections
With the AVC/H.264 High 4:2:2 Profile (compatible with the 4:2:2 chroma format), it is possible to transmit video data containing twice as much color information as is possible with the AVC/H.264 High Profile (incompatible with the 4:2:2 chroma format), which is often used for video transmission. Consequently, with the support of the AVC/H.264 High 4:2:2 Profile, the HV9100 Series HDTV/SDTV encoder/decoder is capable of transmitting video image with minimum image quality degradation even when it is used in cascaded codec connection.